Ubuntu 新建用户 Shell 命令行显示异常
相关环境
Ubuntu 20.04
问题描述
在使用 Ubuntu 系统 root 用户创建一个普通用户后,发现 Shell 命令行显示很简单,不显示用户名、hostname等信息。
root@ecszjk:~# useradd test -m
root@ecszjk:~#
root@ecszjk:~#
root@ecszjk:~# su - test
$
$ id
uid=1001(test) gid=1001(test) groups=1001(test)
$
问题原因
这个问题是由于新创建的用户默认使用的是 /bin/sh 而不是 /bin/bash,两种不同规范的 Shell 不一样。
可以从 /etc/passwd 中查看账号的 Shell 命令,从 /etc/passwd 中可以看到默认创建的用户使用的是 /bin/sh,而 root 用户使用的是 /bin/bash。
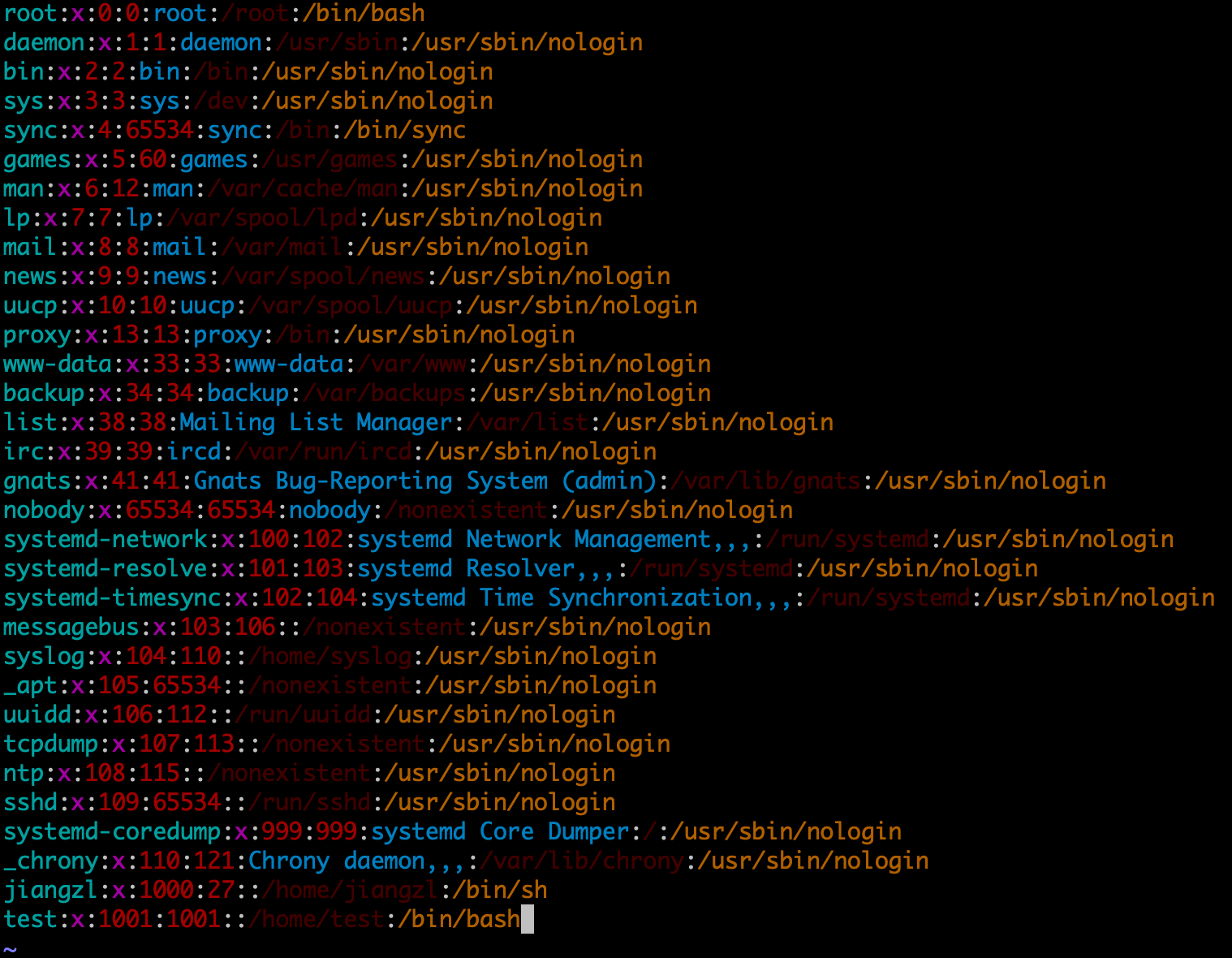
$ cat /etc/passwd
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
...
test:x:1001:1001::/home/test:/bin/sh
解决方法
方法一:
使用 root 用户编辑 /etc/passwd 文件,将对应用户的 Shell 改为 /bin/bash,并保存退出
root@ecszjk:/etc# vim /etc/passwd
使用 vim 的命令模式输入 :wq 保存并退出。
方法二:
使用 root 用户执行 usermod 命令为对应用户更新 Shell
root@ecszjk:~#
root@ecszjk:~# usermod test -s /bin/bash
root@ecszjk:~# cat /etc/passwd
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
...
test:x:1001:1001::/home/test:/bin/bash
附录
1、useradd 用法
root@ecszjk:/etc# useradd --help
Usage: useradd [options] LOGIN
useradd -D
useradd -D [options]
Options:
--badnames do not check for bad names
-b, --base-dir BASE_DIR base directory for the home directory of the
new account
--btrfs-subvolume-home use BTRFS subvolume for home directory
-c, --comment COMMENT GECOS field of the new account
-d, --home-dir HOME_DIR home directory of the new account
-D, --defaults print or change default useradd configuration
-e, --expiredate EXPIRE_DATE expiration date of the new account
-f, --inactive INACTIVE password inactivity period of the new account
-g, --gid GROUP name or ID of the primary group of the new
account
-G, --groups GROUPS list of supplementary groups of the new
account
-h, --help display this help message and exit
-k, --skel SKEL_DIR use this alternative skeleton directory
-K, --key KEY=VALUE override /etc/login.defs defaults
-l, --no-log-init do not add the user to the lastlog and
faillog databases
-m, --create-home create the user's home directory
-M, --no-create-home do not create the user's home directory
-N, --no-user-group do not create a group with the same name as
the user
-o, --non-unique allow to create users with duplicate
(non-unique) UID
-p, --password PASSWORD encrypted password of the new account
-r, --system create a system account
-R, --root CHROOT_DIR directory to chroot into
-P, --prefix PREFIX_DIR prefix directory where are located the /etc/* files
-s, --shell SHELL login shell of the new account
-u, --uid UID user ID of the new account
-U, --user-group create a group with the same name as the user
-Z, --selinux-user SEUSER use a specific SEUSER for the SELinux user mapping
--extrausers Use the extra users database
2、/bin/sh 与 /bin/bash 的区别

近期评论